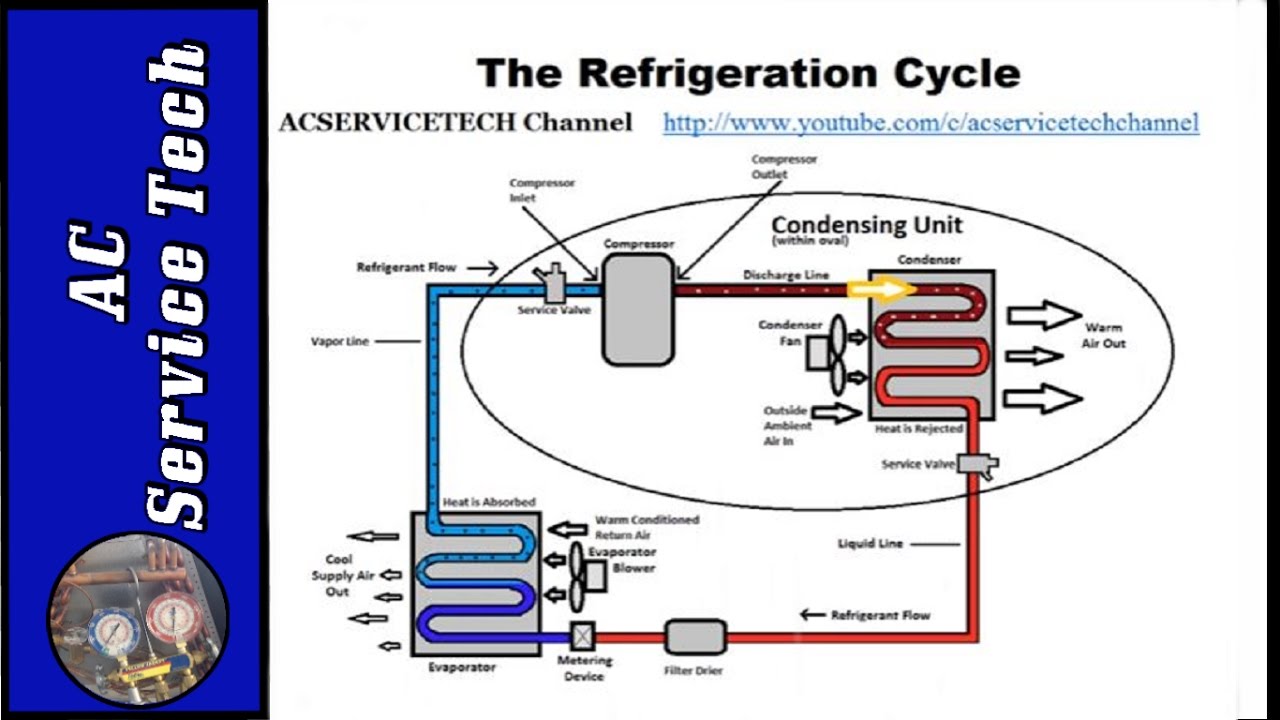
Superheat is the temperature rise of a vapor above its boiling point. Subcooling is the cooling of a liquid below its condensation point.
Superheat and subcooling are crucial concepts in HVAC systems. They ensure efficient operation and prevent damage. Superheat involves raising the temperature of a refrigerant vapor above its boiling point. This process helps in preventing liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor, which can cause damage.
Subcooling, on the other hand, involves cooling the liquid refrigerant below its condensation point. This enhances the system’s efficiency by ensuring the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the expansion valve. Both processes are essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of HVAC systems. Proper measurement and control of superheat and subcooling can lead to energy savings and improved system reliability.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Introduction To Hvac Efficiency
HVAC systems play a vital role in maintaining comfort in homes and offices. Understanding HVAC efficiency is crucial to ensure they work optimally. This guide will help you grasp the basics of superheat and subcooling.
Importance Of Efficiency
Efficient HVAC systems save energy and reduce utility bills. They also provide better indoor air quality and comfort. Ensuring your system is efficient can extend its lifespan.
- Energy Savings: Efficient systems use less power.
- Cost Reduction: Lower energy usage means lower bills.
- Enhanced Comfort: Proper efficiency maintains consistent temperatures.
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of HVAC efficiency involves two key terms: superheat and subcooling. These terms relate to the refrigerant’s state within the system.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Superheat | The temperature of the vapor above its boiling point. |
| Subcooling | The temperature of the liquid below its condensing point. |
Superheat ensures the refrigerant is fully vaporized before reaching the compressor. Subcooling ensures the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the expansion valve.
- Check superheat to avoid compressor damage.
- Check subcooling to ensure efficient heat exchange.
Regular maintenance can help monitor these parameters. This ensures your HVAC system runs efficiently.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Superheat Basics
Understanding superheat is crucial for anyone working in HVAC systems. It’s a key concept that ensures the system operates efficiently. Superheat involves the process of heating refrigerant vapor above its boiling point. This section will cover the basics of superheat, including its definition and its role in HVAC systems.
Definition
Superheat is the temperature increase of refrigerant vapor above its saturation point. For example, if the refrigerant boils at 40°F and the vapor reaches 50°F, the superheat is 10°F. Superheat ensures that only vapor, not liquid, enters the compressor.
Role In Hvac Systems
Superheat plays a vital role in HVAC systems. It helps prevent compressor damage by ensuring no liquid refrigerant enters. This is crucial because liquid in the compressor can cause mechanical failure.
| Superheat Range | System Status |
|---|---|
| 0-5°F | Potential liquid in compressor |
| 5-20°F | Optimal range |
| 20+°F | System may be undercharged |
The ideal superheat range is between 5°F and 20°F. This ensures the system runs efficiently and safely. High superheat can indicate an undercharged system. Low superheat can signal overcharging or other issues.
- Prevents compressor damage
- Ensures efficient system operation
- Indicates potential system issues
Monitoring superheat is essential for maintaining an HVAC system. It helps in diagnosing issues early, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
Measuring Superheat
Understanding superheat is crucial for HVAC technicians. It ensures the system runs efficiently. Measuring superheat helps diagnose issues and maintain optimal performance. Follow this guide to measure superheat accurately.
Required Tools
Before starting, gather these essential tools:
- Digital thermometer
- Pressure gauge
- Superheat calculator
Ensure all tools are in good working condition. Calibration is essential for accurate readings.
Measurement Process
Follow these steps to measure superheat:
- Locate the suction line near the evaporator outlet.
- Attach the pressure gauge to the suction line service port.
- Read the pressure from the gauge. Note this value.
- Use the superheat calculator to find the saturation temperature.
- Place the digital thermometer on the suction line.
- Record the actual temperature from the thermometer.
- Calculate the superheat. Subtract the saturation temperature from the actual temperature.
Ensure all readings are accurate. Incorrect readings can lead to system malfunction.
Following these steps ensures accurate superheat measurement. This maintains your HVAC system’s efficiency and reliability.
Subcooling Fundamentals
Understanding subcooling fundamentals is essential for efficient HVAC systems. Subcooling ensures your system runs smoothly and efficiently. Let’s delve into the basics of subcooling and its impact on performance.
Definition
Subcooling refers to cooling a liquid below its condensation point. In HVAC systems, it means cooling the refrigerant below its saturation temperature. This process occurs after the refrigerant leaves the condenser. It ensures the refrigerant is in a liquid state before entering the expansion valve.
Impact On Performance
Proper subcooling improves system performance significantly. Here are some key impacts:
- Energy Efficiency: Subcooling increases energy efficiency, reducing energy bills.
- System Reliability: It prevents compressor damage, enhancing system reliability.
- Cooling Capacity: Subcooling ensures the system achieves maximum cooling capacity.
Let’s understand these impacts in detail.
Energy Efficiency
Subcooling enhances energy efficiency by reducing the compressor’s workload. A properly subcooled refrigerant means the compressor doesn’t work as hard. This leads to lower energy consumption and cost savings.
System Reliability
Subcooling safeguards the compressor from damage. It ensures only liquid refrigerant reaches the expansion valve. This prevents vapor from entering the compressor, reducing wear and tear.
Cooling Capacity
Subcooling maximizes the cooling capacity of the HVAC system. A subcooled refrigerant absorbs more heat, improving overall cooling performance. This ensures your space remains comfortable and cool.
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy consumption by lowering the compressor’s workload. |
| System Reliability | Prevents compressor damage by ensuring only liquid refrigerant enters. |
| Cooling Capacity | Increases the system’s ability to absorb heat, enhancing performance. |
Calculating Subcooling
Understanding how to calculate subcooling is crucial for efficient HVAC system operation. Subcooling refers to the cooling of a liquid refrigerant below its condensation point. This ensures the refrigerant is fully in liquid form before entering the evaporator. This process helps in efficient system performance and energy savings.
Necessary Instruments
Before starting the calculation, gather the necessary instruments. These tools are essential for accurate readings.
- Pressure gauge – Measures the system pressure.
- Thermometer – Measures the refrigerant temperature.
- Subcooling calculator or chart – For quick reference.
Step-by-step Guide
Follow these steps to calculate subcooling accurately:
- Attach the pressure gauge to the high side of the system.
- Read and note the pressure from the gauge.
- Convert the pressure reading to temperature using a PT chart.
- Measure the actual temperature of the liquid line using a thermometer.
- Subtract the actual temperature from the converted temperature.
Here is a simple table for better understanding:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Attach pressure gauge |
| 2 | Note pressure reading |
| 3 | Convert pressure to temperature |
| 4 | Measure liquid line temperature |
| 5 | Subtract actual temperature from converted temperature |
By following these steps, you can ensure your HVAC system runs efficiently. Proper subcooling improves system performance and longevity.
Balancing Superheat And Subcooling
Balancing superheat and subcooling is crucial for HVAC systems. Proper balance ensures efficient cooling and heating. It prevents system failures and reduces energy costs.
Optimal Levels
Maintaining optimal levels of superheat and subcooling is key. Superheat should ideally be between 10-20 degrees Fahrenheit. Subcooling should be between 8-12 degrees Fahrenheit. These ranges ensure the system operates efficiently.
| Parameter | Optimal Range (°F) |
|---|---|
| Superheat | 10-20 |
| Subcooling | 8-12 |
Adjustment Techniques
Adjusting superheat and subcooling involves several techniques. Here are some common methods:
- Superheat Adjustment:
- Adjust the thermal expansion valve (TXV).
- Check for proper refrigerant charge.
- Ensure no blockages or restrictions in the system.
- Subcooling Adjustment:
- Verify correct refrigerant levels.
- Inspect the condenser coil for dirt or debris.
- Ensure the condenser fan is working properly.
Regular maintenance helps in maintaining these levels. Technicians should use proper tools like gauges and thermometers. This ensures accurate readings.
Common Issues And Solutions
Superheat and subcooling are vital in HVAC systems. They ensure efficiency and performance. But, they can face issues. Here are common problems and their solutions.
Superheat Problems
Superheat problems can reduce efficiency. It may also damage the system. Understanding these problems is crucial.
- Low Superheat: This can indicate an overcharged system. It may also mean restricted airflow.
- High Superheat: This often means a low refrigerant charge. Another cause could be a blocked evaporator coil.
Addressing these issues can restore system performance. Here are solutions:
- Check Refrigerant Charge: Ensure the system has the correct refrigerant amount.
- Inspect Airflow: Ensure filters and coils are clean.
- Monitor Temperature: Use precise tools to measure superheat levels.
Subcooling Challenges
Subcooling issues can affect cooling efficiency. They can also strain the system.
- Low Subcooling: This may mean the system is undercharged.
- High Subcooling: This could indicate an overcharged system.
Fixing these problems can improve system efficiency. Here are solutions:
- Adjust Refrigerant Levels: Ensure the refrigerant is at the correct level.
- Check for Blockages: Ensure there are no obstructions in the condenser coil.
- Monitor System Performance: Regularly check subcooling levels with accurate tools.
By addressing these superheat and subcooling issues, HVAC systems can run efficiently. Regular maintenance and monitoring are key to preventing problems.
Advanced Tips For Efficiency
Optimizing superheat and subcooling is crucial for HVAC system efficiency. Advanced tips can maximize performance and longevity. Below are some professional insights and maintenance practices to help you achieve this.
Professional Insights
- Monitor regularly: Regular checks ensure system efficiency.
- Use the right tools: Invest in quality gauges and thermometers.
- Understand system specifics: Know the manufacturer’s recommended superheat and subcooling levels.
Maintenance Practices
| Task | Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Check refrigerant levels | Monthly | Ensure levels are within the recommended range. |
| Clean condenser coils | Quarterly | Dirty coils can affect subcooling efficiency. |
| Inspect insulation | Bi-annually | Check for wear and tear to prevent heat loss. |
- Keep records: Document maintenance activities.
- Train staff: Ensure team members understand the importance of superheat and subcooling.
Credit: m.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Superheat In Hvac?
Superheat is the temperature of vapor refrigerant above its boiling point. It ensures the refrigerant is fully vaporized before entering the compressor.
What Is Subcooling In Refrigeration?
Subcooling is the temperature of liquid refrigerant below its condensation point. It ensures the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the expansion valve.
Why Is Superheat Important?
Superheat prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor. This protects the compressor from damage and increases system efficiency.
Why Is Subcooling Necessary?
Subcooling ensures that only liquid refrigerant enters the expansion valve. This improves system efficiency and prevents potential damage to the components.
Conclusion
Mastering superheat and subcooling ensures efficient HVAC systems. These concepts boost performance and reduce energy costs. Understanding them improves troubleshooting and maintenance. Proper knowledge leads to better system longevity. Stay informed and keep your HVAC systems running smoothly.
