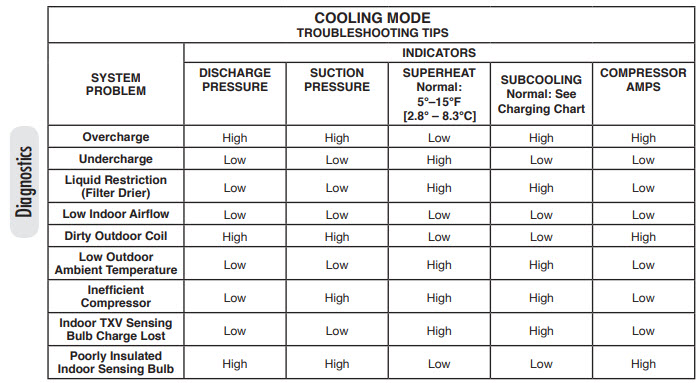
Low superheat with normal subcooling often indicates an overcharged system or restricted airflow. Proper diagnosis is crucial to prevent system damage.
Low superheat and normal subcooling are key indicators in HVAC systems. Understanding these metrics helps in diagnosing potential issues efficiently. Low superheat suggests that the evaporator coil is not absorbing enough heat, which can result from excess refrigerant or insufficient airflow.
Normal subcooling indicates that the refrigerant is being properly condensed. This combination often points to an overcharged system or airflow restrictions. Addressing these issues promptly ensures the HVAC system operates efficiently and prevents potential damage. Regular maintenance and accurate diagnostics are essential for optimal performance and longevity of the HVAC system. Properly interpreting these readings can save time and reduce repair costs.
Understanding Superheat
Superheat plays a critical role in HVAC systems. It ensures the refrigerant is fully vaporized. This prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor. Understanding superheat helps diagnose system issues.
Definition And Role
Superheat is the temperature of the refrigerant vapor above its boiling point. It’s measured at the evaporator outlet. It indicates how much heat the refrigerant has absorbed. Proper superheat levels ensure efficient system operation.
The role of superheat includes:
- Preventing compressor damage.
- Ensuring complete vaporization of the refrigerant.
- Optimizing system efficiency.
A correct superheat setting maintains system health. It also avoids energy wastage.
Symptoms Of Low Superheat
Low superheat indicates a problem in the system. Here are some symptoms:
- Frost on evaporator coils: Indicates liquid refrigerant is not fully vaporized.
- High compressor discharge temperature: Shows the compressor is working harder.
- Reduced cooling efficiency: Results in longer cooling cycles.
- Increased energy consumption: Due to the compressor running more.
These symptoms can lead to system failure. Regular checks help maintain proper superheat levels.
Credit: abrwholesalers.com
Understanding Subcooling
Subcooling is a crucial concept in the world of HVAC. It ensures efficient cooling and proper functioning of your system. Understanding subcooling can help you maintain and troubleshoot your HVAC system better.
Definition And Role
Subcooling refers to the process of cooling a liquid below its condensation temperature. This occurs without it becoming a gas again. In HVAC systems, subcooling happens when the refrigerant is cooled after it has condensed from a gas to a liquid.
Subcooling plays a vital role in the efficiency of your HVAC system. It ensures that the refrigerant is in the right state before it enters the evaporator. This maximizes the cooling effect and enhances system efficiency.
Normal Subcooling Levels
Maintaining normal subcooling levels is essential for the proper function of your HVAC system. These levels usually range between 10°F to 20°F. This range can vary based on the specific system and its requirements.
Here is a quick reference table for typical subcooling levels:
| System Type | Normal Subcooling Range (°F) |
|---|---|
| Residential HVAC | 10-15 |
| Commercial HVAC | 15-20 |
Regular monitoring of subcooling levels helps in early detection of potential issues. This can prevent costly repairs and system downtime.
To measure subcooling, follow these simple steps:
- Attach the temperature probe to the liquid line.
- Read the liquid line temperature.
- Compare it to the saturation temperature.
- Calculate the difference to determine subcooling.
Proper subcooling ensures that your HVAC system runs efficiently. It prevents issues such as compressor overheating and inefficient cooling.
Causes Of Low Superheat
Understanding the causes of low superheat is essential for maintaining efficient HVAC systems. Low superheat can indicate several underlying issues that need immediate attention. Below, we explore the primary causes in detail.
Refrigerant Overcharge
One common cause of low superheat is refrigerant overcharge. Overcharging occurs when the system has more refrigerant than needed. This excess refrigerant leads to low superheat levels.
Signs of refrigerant overcharge include:
- High suction pressure
- Low superheat
- Poor cooling performance
To correct refrigerant overcharge, technicians must remove the excess refrigerant. Ensure the charge is within manufacturer specifications.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve Issues
The Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) plays a crucial role in regulating refrigerant flow. Problems with the TXV can cause low superheat.
Common TXV issues include:
- Stuck valve
- Improper adjustment
- Blocked sensing bulb
To address TXV problems, first check for proper adjustment. Ensure the sensing bulb is correctly attached and not blocked. If issues persist, consider replacing the TXV.
Impacts On Hvac Performance
Understanding the impacts on HVAC performance is crucial for optimal system operation. Low superheat and normal subcooling can significantly affect energy efficiency and system longevity. This section explores these impacts in detail.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is vital for reducing operational costs. Low superheat indicates excessive refrigerant in the evaporator. This condition can lead to inefficient cooling cycles. The compressor works harder, consuming more energy.
Normal subcooling ensures the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the evaporator. While this is good, low superheat can negate these benefits. The system may struggle to maintain desired temperatures.
Regular maintenance helps balance superheat and subcooling levels. This practice ensures optimal energy use. Proper adjustments can lead to significant energy savings.
System Longevity
System longevity is another critical aspect. Low superheat can cause liquid refrigerant to enter the compressor. This situation, known as liquid slugging, can damage the compressor over time.
Normal subcooling helps protect the compressor by ensuring liquid refrigerant is adequately managed. But, low superheat still poses risks. Over time, this imbalance can lead to frequent repairs and reduced system lifespan.
A balanced HVAC system runs smoother and lasts longer. Regular checks and adjustments are essential. Ensuring proper superheat and subcooling levels can extend the life of your system.
Diagnosing Low Superheat
Diagnosing low superheat in an HVAC system is crucial. It helps in maintaining efficiency and preventing damage. This guide will show you the tools needed and the step-by-step process to diagnose low superheat.
Tools Required
- Thermometer: To measure the temperature.
- Pressure Gauge: To read the system pressure.
- Multimeter: To check electrical components.
- Thermocouple: For accurate temperature readings.
- Refrigerant Scale: To measure refrigerant levels.
Step-by-step Process
- Check the Thermostat: Ensure it is set correctly.
- Measure Ambient Temperature: Use a thermometer for this step.
- Attach Pressure Gauge: Connect it to the low-side service port.
- Read Pressure: Note the reading from the gauge.
- Measure Evaporator Outlet Temperature: Use a thermocouple.
- Calculate Superheat: Subtract the evaporator temperature from the ambient temperature.
- Analyze the Results: Compare your superheat reading with the recommended range.
| Step | Action | Tool Needed |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Check the Thermostat | None |
| 2 | Measure Ambient Temperature | Thermometer |
| 3 | Attach Pressure Gauge | Pressure Gauge |
| 4 | Read Pressure | Pressure Gauge |
| 5 | Measure Evaporator Outlet Temperature | Thermocouple |
| 6 | Calculate Superheat | None |
| 7 | Analyze the Results | None |
Credit: www.reddit.com
Solutions For Low Superheat
Low superheat can signal issues in your refrigeration system. Addressing these problems ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency. Below are some effective solutions for low superheat.
Adjusting Refrigerant Levels
Proper refrigerant levels are crucial. Low refrigerant can cause low superheat.
- Check the refrigerant charge using a gauge set.
- Ensure the system has the correct refrigerant type.
- Add or remove refrigerant as needed.
Monitoring refrigerant levels helps maintain system efficiency. Keeping them balanced prevents further issues.
Checking And Replacing Components
Faulty components can lead to low superheat. Inspect these parts:
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV)
- Evaporator Coils
- Filter Drier
Ensure the TXV is functioning. A malfunctioning TXV can cause improper refrigerant flow.
Clean or replace the evaporator coils if dirty or damaged. Blocked coils affect heat absorption.
Replace the filter drier if it’s clogged. A clogged filter drier restricts refrigerant flow.
Maintaining Optimal Hvac Efficiency
Maintaining your HVAC system ensures it runs efficiently. Low superheat and normal subcooling indicate a well-functioning system. This balance improves comfort and saves energy. Regular checks and professional inspections are key.
Regular Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps your HVAC system in top shape. Follow these simple tips:
- Change filters every three months for better airflow.
- Keep the outdoor unit clean to prevent debris buildup.
- Check for refrigerant leaks to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect ductwork for any obstructions or damage.
These simple tasks can prolong your system’s life. They also ensure it performs optimally.
Professional Inspection Benefits
Professional inspections offer deeper insights into your HVAC system. Here are the benefits:
- Thorough checks by certified technicians.
- Identify and fix potential issues before they worsen.
- Ensure optimal refrigerant levels for efficiency.
- Receive expert advice on system upgrades and improvements.
Professional services can save you money in the long run. They help maintain the balance of low superheat and normal subcooling.

Credit: yorkcentraltechtalk.wordpress.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Low Superheat?
Low superheat is caused by an oversized or malfunctioning expansion valve. It can also result from a refrigerant overcharge or low airflow.
How To Fix Low Superheat Issue?
To fix low superheat, check and adjust the expansion valve. Ensure proper refrigerant charge and verify adequate airflow over the evaporator.
What Does Normal Subcooling Indicate?
Normal subcooling indicates the condenser is removing heat effectively. It suggests proper refrigerant charge and efficient system operation.
Can Low Superheat Damage The Compressor?
Yes, low superheat can damage the compressor. It can cause liquid refrigerant to enter, leading to potential failure.
Conclusion
Understanding low superheat and normal subcooling is crucial for HVAC efficiency. These parameters ensure optimal system performance. Regular monitoring can prevent costly repairs. Keep your HVAC system in top condition for energy savings. Proper maintenance leads to longer equipment life and better comfort.
Stay informed and enjoy a reliable HVAC system.
