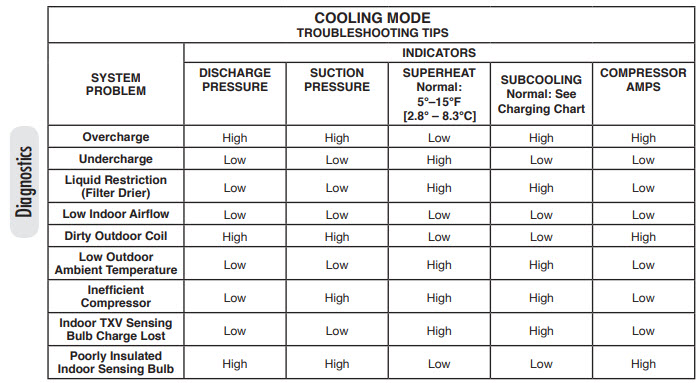
Low superheat and low subcooling often indicate an overcharged system or a malfunctioning metering device. This can lead to inefficient cooling and potential damage to the HVAC system.
Low superheat and low subcooling are crucial indicators in HVAC systems. They help diagnose issues related to refrigerant charge and system efficiency. Low superheat usually means the evaporator coil is getting too much refrigerant, leading to poor heat absorption. Low subcooling indicates insufficient heat removal in the condenser, causing inefficient cooling.
Both conditions can result from an overcharged system, malfunctioning metering devices, or other mechanical issues. Prompt diagnosis and correction are essential to maintain system performance and prevent long-term damage. Understanding these parameters can help technicians ensure the HVAC system operates efficiently and reliably.
Introduction To Hvac Efficiency
HVAC systems are vital for our comfort. They control the air temperature and quality. Efficient HVAC systems save energy and money. They also reduce environmental impact.
Importance Of Efficiency
Efficiency in HVAC systems means using less energy to achieve the same comfort. This saves on electricity bills. It also lessens the wear and tear on the system. An efficient system runs smoothly. It lasts longer and needs fewer repairs.
Efficient systems are good for the environment. They reduce carbon footprints. They help in conserving natural resources. Everyone benefits from an efficient HVAC system.
Basic Concepts
Superheat and subcooling are key concepts in HVAC efficiency. Superheat is the temperature above the boiling point of the refrigerant. Subcooling is the temperature below the condensing point of the refrigerant.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Superheat | Temperature above the boiling point of refrigerant. |
| Subcooling | Temperature below the condensing point of refrigerant. |
Low superheat means the system is cooling efficiently. Low subcooling means the refrigerant is condensed properly. Both ensure the system works at its best.
- Low superheat ensures the evaporator is fully utilized.
- Low subcooling ensures the condenser works efficiently.
Understanding these concepts helps in maintaining HVAC systems. It helps in diagnosing problems early. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Understanding Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding superheat and subcooling is essential in HVAC systems. These terms help diagnose system performance issues. Let’s dive into their definitions.
Superheat Defined
Superheat is the temperature rise above a refrigerant’s boiling point. It occurs in the evaporator coils. Superheat ensures no liquid refrigerant returns to the compressor. Measuring superheat helps in system efficiency.
Superheat = (Actual Temperature - Boiling Point)Using gauges, measure the evaporator outlet temperature. Compare it with the boiling point.
Subcooling Defined
Subcooling is the temperature drop below a refrigerant’s condensing point. It happens in the condenser coils. Subcooling ensures all vapor turns back to liquid. Proper subcooling prevents compressor damage.
Subcooling = (Condensing Temperature - Actual Temperature)Use gauges to measure the condenser outlet temperature. Compare it with the condensing temperature.
| Term | Definition | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Superheat | Temperature rise above boiling point | Evaporator coils |
| Subcooling | Temperature drop below condensing point | Condenser coils |
Impact Of Low Superheat
Low superheat in an HVAC system can lead to various problems. This section explores how low superheat affects system performance and potential issues it might cause.
System Performance
Low superheat can negatively impact system performance. It means that the refrigerant is not properly vaporized. This can lead to inefficient cooling.
When superheat is low, the compressor might struggle. This reduces the lifespan of the system. The energy consumption also increases, leading to higher bills.
| Performance Metrics | Impact |
|---|---|
| Cooling Efficiency | Decreased |
| Compressor Lifespan | Reduced |
| Energy Consumption | Increased |
Potential Issues
Low superheat can cause multiple potential issues. One major issue is liquid refrigerant entering the compressor. This can cause damage to the compressor.
- Compressor damage
- Increased energy bills
- Poor cooling performance
Another issue is frost on the evaporator coils. This can lead to restricted airflow. Restricted airflow reduces system efficiency and performance.
Regular maintenance and proper system checks are essential. These practices help in identifying and correcting low superheat issues.
Impact Of Low Subcooling
Understanding the impact of low subcooling in HVAC systems is crucial. It affects both energy consumption and system reliability. Let’s delve deeper into these aspects.
Energy Consumption
Low subcooling increases energy consumption. The compressor works harder to maintain temperatures. This leads to higher electricity bills.
For instance, consider a table showing the energy impact:
| Subcooling Level | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|
| Normal | Low |
| Low | High |
Low subcooling means more energy usage. This is not efficient.
System Reliability
Low subcooling affects system reliability. The HVAC system may face frequent breakdowns. This leads to increased maintenance costs.
Common issues due to low subcooling include:
- Compressor failure
- Refrigerant leaks
- Reduced cooling efficiency
Maintaining proper subcooling levels is vital. It ensures the system runs smoothly.
To enhance reliability:
- Check subcooling levels regularly.
- Schedule routine maintenance.
- Use quality refrigerants.
Proper subcooling levels keep the system efficient. This reduces unexpected failures.
Balancing Superheat And Subcooling
Balancing superheat and subcooling is crucial for efficient HVAC systems. This process ensures your air conditioning unit runs smoothly. Both superheat and subcooling need to be at optimal levels for the best performance.
Optimal Levels
Keeping superheat and subcooling at optimal levels prevents system issues. Ideal superheat levels range between 10°F to 20°F. Ideal subcooling levels range between 10°F to 20°F. Maintaining these levels enhances system efficiency. Use a chart or table to track these values.
| Measurement | Optimal Range (°F) |
|---|---|
| Superheat | 10 – 20 |
| Subcooling | 10 – 20 |
Measurement Techniques
Accurate measurement techniques are vital for balancing superheat and subcooling. Here are some steps to follow:
- Use a reliable thermometer to measure temperatures.
- Measure the temperature of the suction line for superheat.
- Measure the temperature of the liquid line for subcooling.
- Compare readings with optimal levels using a chart.
Regular checks ensure your system stays efficient. Adjust settings as needed to maintain balance.
Advanced Techniques For Optimization
Optimizing HVAC systems requires advanced techniques. Low superheat and low subcooling are key aspects. These advanced techniques ensure efficient system performance. Let’s explore these methods in detail.
Using Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in optimization. They provide accurate measurements. Temperature sensors help monitor superheat levels. Pressure sensors are essential for subcooling accuracy. These sensors ensure real-time data collection.
| Sensor Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Temperature Sensors | Monitor Superheat Levels |
| Pressure Sensors | Ensure Subcooling Accuracy |
Using these sensors, technicians can make precise adjustments. This leads to energy savings and better performance.
Control Systems
Control systems are vital for system optimization. They automate adjustments and ensure stability. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are commonly used. These controllers manage both superheat and subcooling efficiently.
- Automate adjustments
- Ensure system stability
- Enhance energy efficiency
Control systems can integrate with sensors. This integration offers a comprehensive solution. Technicians can monitor and adjust settings remotely. This provides convenience and saves time.
Advanced techniques like these are essential. They ensure the HVAC system runs efficiently. Proper sensor usage and control systems are key. They help maintain low superheat and low subcooling levels effectively.
Common Challenges And Solutions
Low superheat and low subcooling can cause serious HVAC issues. These problems often affect system efficiency and performance. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant can cause low superheat and subcooling.
- Inspect for Leaks: Leaks in the system can lead to low refrigerant.
- Examine the TXV: A faulty TXV can cause improper refrigerant flow.
- Look at the Evaporator Coil: A dirty coil can affect heat exchange.
Maintenance Practices
| Action | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check Refrigerant Levels | Monthly |
| Clean Evaporator Coil | Quarterly |
| Inspect for Leaks | Monthly |
| Test TXV Function | Annually |
Regular maintenance can prevent low superheat and subcooling. Follow these practices to keep your system efficient.
Case Studies
Exploring real-world scenarios can help understand the impact of Low Superheat Low Subcooling in HVAC systems. Let’s dive into some case studies that illustrate successful implementations and lessons learned.
Successful Implementations
Many HVAC systems have benefited from Low Superheat Low Subcooling. Here are a few notable examples:
- Commercial Building in New York: The building saw a 20% increase in energy efficiency. This was achieved by optimizing the superheat and subcooling settings. The maintenance team reported fewer system failures.
- Residential Complex in California: Residents experienced improved cooling performance. The system operated at lower energy costs. The complex also saw a reduction in repair calls.
- Industrial Plant in Texas: The plant’s refrigeration system became more reliable. Energy consumption dropped by 15%. They also extended the equipment’s lifespan.
Lessons Learned
From these implementations, several key lessons emerged:
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent monitoring is crucial. It ensures the system maintains optimal superheat and subcooling levels.
- Training Technicians: Well-trained technicians can make a significant difference. They can identify and rectify issues promptly.
- Quality Equipment: Using high-quality components is essential. It helps achieve and maintain desired performance levels.
By following these insights, other systems can also achieve better performance and efficiency.
Future Trends In Hvac Efficiency
HVAC systems are evolving rapidly. The focus is on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Low superheat and low subcooling are key areas. They play a crucial role in the system’s performance. Let’s explore the future trends in HVAC efficiency.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies are shaping the HVAC industry. They aim to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Some of the most promising technologies include:
- Smart Thermostats: These devices learn and adapt to user preferences.
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF): VRF systems adjust the refrigerant flow based on demand.
- IoT Integration: Internet of Things (IoT) connects HVAC systems for better monitoring.
These technologies promise significant energy savings. They also improve user comfort and system reliability.
Sustainability Focus
Sustainability is a major focus in HVAC advancements. Reducing the environmental impact is crucial. Key initiatives include:
- Use of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: These refrigerants have a lower global warming potential.
- Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV): ERV systems recover energy from exhaust air.
- Solar-Powered HVAC Systems: These systems use solar energy to operate.
These efforts contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. They also align with global energy-saving goals.
Credit: abrwholesalers.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Low Superheat?
Low superheat indicates that the refrigerant is not fully vaporized. This can affect the efficiency of the HVAC system.
Why Is Low Superheat A Problem?
Low superheat can lead to liquid refrigerant entering the compressor. This can cause mechanical damage and reduce system efficiency.
What Causes Low Superheat In Hvac Systems?
Low superheat is often caused by overcharging the system with refrigerant. Other causes include blocked evaporator coils and malfunctioning expansion valves.
What Is Low Subcooling?
Low subcooling means the refrigerant is not adequately cooled after condensation. This can affect the system’s performance.
Conclusion
Understanding low superheat and low subcooling is crucial for efficient HVAC systems. It helps maintain optimal performance. Regular maintenance ensures energy efficiency and longevity. By monitoring these parameters, you can prevent costly repairs. Keep your system running smoothly and effectively.
Stay informed for better HVAC management.
