To measure superheat, use a digital manifold gauge to read the suction line temperature and corresponding pressure. Subtract the saturation temperature from the suction line temperature.
Superheat measurement is crucial for HVAC system efficiency and reliability. It ensures that the refrigerant vaporizes completely, preventing liquid refrigerant from damaging the compressor. Technicians frequently measure superheat to diagnose system performance and ensure optimal operation. Accurate superheat readings help in fine-tuning the system for energy efficiency and longevity.
Properly measuring superheat can also reveal potential issues such as refrigerant undercharge or overcharge. Understanding and measuring superheat correctly can significantly improve system performance, leading to better cooling and energy savings. This skill is essential for any HVAC professional looking to maintain or improve system efficiency.
Introduction To Superheat
Superheat is a vital concept in the world of HVAC systems. Understanding superheat ensures efficient and safe operation. This section explores what superheat is and why it matters.
Definition
Superheat is the temperature above the boiling point of a liquid. In HVAC systems, it refers to the temperature of the refrigerant gas after it has fully vaporized. This is measured at the evaporator outlet.
Importance In Hvac Systems
Superheat is crucial for HVAC system efficiency and safety. Correct superheat levels ensure optimal performance. It prevents liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. This protects the compressor from damage.
| Component | Role | Impact of Incorrect Superheat |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat | Reduced cooling efficiency |
| Compressor | Compresses refrigerant | Risk of damage |
| Condenser | Releases heat | Poor heat rejection |
Superheat also helps in diagnosing system issues. Technicians use it to identify problems like low refrigerant levels or blockages. Proper superheat ensures the system operates smoothly and efficiently.
- Ensures system efficiency
- Prevents compressor damage
- Helps diagnose issues
Understanding superheat is essential for anyone working with HVAC systems. It ensures the system runs efficiently and safely.
Tools Needed
Measuring superheat requires specific tools. You need accurate instruments to get precise readings. The main tools include thermometers and pressure gauges.
Thermometers
Thermometers are essential for measuring temperature. You will need a reliable digital or analog thermometer. Ensure the thermometer can measure both high and low temperatures. Here are some key features:
- Accuracy: Look for a thermometer with a high accuracy rate.
- Range: It should cover a wide temperature range.
- Digital Display: Easier to read than analog.
| Feature | Importance |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | High |
| Range | Wide |
| Digital Display | Optional but useful |
Pressure Gauges
Pressure gauges measure the pressure in the system. You need a gauge compatible with your system. Key features to look for in a pressure gauge include:
- Accuracy: Crucial for reliable readings.
- Durability: Should withstand high pressure.
- Compatibility: Must fit your system’s specifications.
Here’s a quick checklist for choosing a pressure gauge:
- Check the pressure range.
- Ensure it has a clear display.
- Verify compatibility with your system.
Preparation Steps
Measuring superheat is crucial for HVAC system efficiency. Proper preparation is key. Follow these steps to ensure accurate readings and safe operations.
Safety Precautions
Before you start, prioritize safety. Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Wear safety goggles and gloves.
- Ensure the area is well-ventilated.
- Turn off the system and disconnect power.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Use insulated tools to avoid electrical hazards.
System Inspection
Inspect the system thoroughly to avoid errors. Follow these steps:
- Check for visible damage or leaks.
- Ensure all valves are in the correct position.
- Verify the system’s refrigerant level.
- Inspect the condenser and evaporator coils.
- Ensure all electrical connections are secure.
Proper system inspection ensures accurate superheat measurements. It also helps identify potential issues early.
Tools And Equipment
Gather all necessary tools and equipment. Here is a list:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Thermometer | Measure temperature |
| Pressure gauge | Check system pressure |
| Wrench set | Adjust valves |
| Safety gear | Protection |
Having the right tools and equipment ensures efficiency and accuracy in measurements.
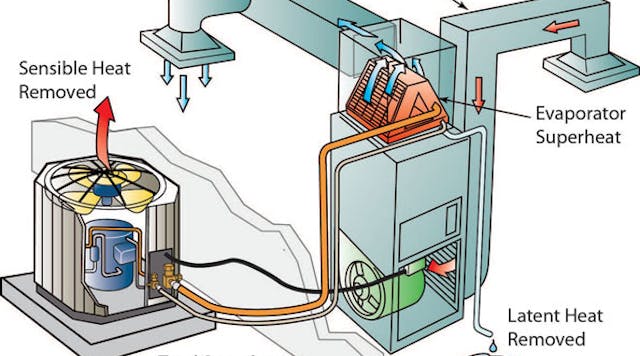
Credit: www.contractingbusiness.com
Measuring Suction Line Temperature
Measuring the suction line temperature is crucial for determining superheat. It ensures the system runs efficiently. Follow these steps to get an accurate reading.
Thermometer Placement
First, locate the suction line. It is usually the larger of the two refrigerant lines.
Wrap the thermometer probe tightly around the suction line. Ensure it is secure to get an accurate reading.
Cover the probe with insulation tape. This helps to avoid external temperature influences.
Reading The Temperature
Wait for the thermometer to stabilize. This might take a few minutes.
Once stable, note the temperature displayed. This is your suction line temperature.
Use the following table to summarize the steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Locate the suction line |
| 2 | Wrap the thermometer probe around the line |
| 3 | Insulate the probe with tape |
| 4 | Wait for the thermometer to stabilize |
| 5 | Read and record the temperature |
These simple steps ensure an accurate suction line temperature measurement. This is essential for calculating superheat.
Determining Evaporator Pressure
Understanding how to measure superheat is crucial for HVAC technicians. One key step is determining the evaporator pressure. This pressure helps gauge the efficiency of the refrigeration system. In this section, we will explore how to set up a pressure gauge and record the pressure accurately.
Pressure Gauge Setup
First, ensure you have a high-quality pressure gauge. Attach the gauge to the low-side service port of the evaporator. Make sure the connection is secure to avoid leaks. Follow these steps:
- Turn off the HVAC system.
- Locate the low-side service port.
- Attach the pressure gauge firmly.
Tip: Ensure the gauge is calibrated correctly.
Recording The Pressure
Once the pressure gauge is set up, turn on the HVAC system. Allow it to run for a few minutes. This stabilizes the pressure readings. Now, record the pressure displayed on the gauge. Use a notepad or digital device for accuracy.
Here is a simple table to help you record the readings:
| Time | Pressure (psi) |
|---|---|
| 8:00 AM | 68 |
| 8:10 AM | 70 |
| 8:20 AM | 72 |
Regularly recording the pressure helps monitor system performance. Keep the readings consistent for best results.
Calculating Superheat
Measuring superheat is crucial for the efficient operation of HVAC systems. Superheat is the temperature of refrigerant gas above its boiling point. Properly calculating superheat ensures the system runs smoothly and avoids damage.
Using Temperature And Pressure Readings
To measure superheat, you need a few tools. You’ll need a pressure gauge and a temperature probe. First, attach the pressure gauge to the suction line. This will give you the pressure reading of the refrigerant.
Next, attach the temperature probe to the same suction line. Ensure the probe is close to the evaporator. This will give you the temperature reading of the refrigerant gas.
Record both the pressure and temperature readings. These readings are essential for calculating superheat.
Superheat Formula
Use the following formula to calculate superheat:
Superheat = Actual Temperature - Saturation TemperatureFollow these steps:
- Find the saturation temperature. Use a refrigerant pressure-temperature chart.
- Locate your pressure reading on the chart. Match it to the corresponding saturation temperature.
- Subtract the saturation temperature from the actual temperature.
For example, if the actual temperature is 55°F and the saturation temperature is 45°F:
Superheat = 55°F - 45°F = 10°FEnsure the superheat value is within the recommended range. This varies by system but typically falls between 10°F and 20°F.
Correct superheat levels optimize system performance. They also prevent compressor damage and ensure energy efficiency.
Adjusting Superheat Levels
Adjusting superheat levels is crucial for the efficient operation of HVAC systems. Proper adjustments ensure the system runs efficiently and prevents damage.
Fine-tuning The System
To fine-tune the system, you need specific tools. Use a superheat gauge and a thermometer.
Follow these steps:
- Attach the superheat gauge to the suction line.
- Place the thermometer on the same line.
- Read both the pressure and temperature values.
Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s recommended values. Adjust the expansion valve if the superheat is too high or too low.
Rechecking Measurements
After making adjustments, recheck the measurements. Repeat the process to ensure accuracy.
Use the table below to record your measurements:
| Measurement | Initial Value | Adjusted Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure (PSI) | ||
| Temperature (°F) |
Ensure the new values are within the acceptable range. Repeat adjustments if necessary.
Recording and rechecking measurements helps maintain system efficiency. This practice extends the life of your HVAC system.
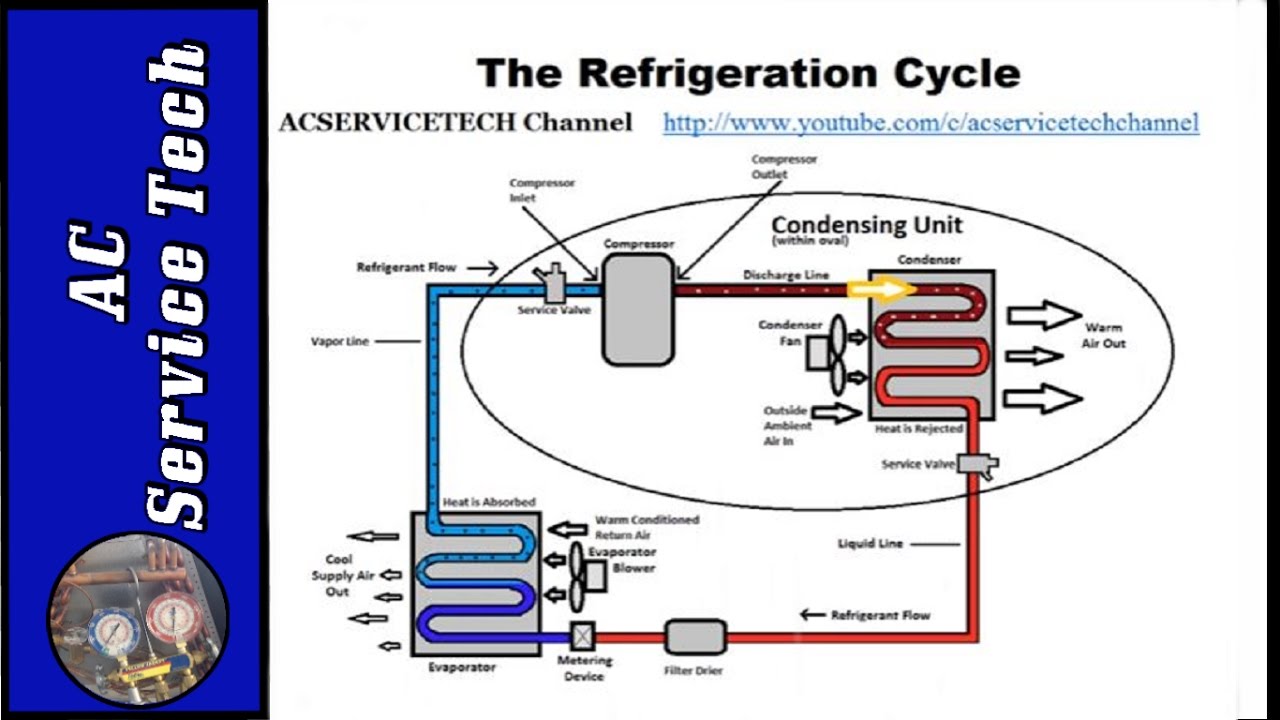
Credit: m.youtube.com
Common Mistakes
Measuring superheat is crucial for HVAC systems. It helps ensure efficiency and prevents damage. Many technicians make mistakes during this process. Avoiding these common errors can save time and money.
Incorrect Thermometer Placement
Placing the thermometer incorrectly is a frequent mistake. The thermometer should be on the suction line. Ensure it is placed between 6 to 8 inches from the compressor. This helps get accurate readings.
Improper placement can lead to false readings. False readings affect the superheat calculation. Always double-check the thermometer’s position.
Improper Gauge Usage
Using the gauge incorrectly is another common error. Gauges measure pressure and are essential for superheat calculations. Always ensure the gauges are calibrated correctly. Incorrect calibration leads to inaccurate results.
Connect the gauge to the correct port. The low-side port is for the suction line. Wrong connections can give wrong pressure readings.
Additionally, make sure to read the gauge correctly. Misreading can skew the superheat measurement. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for accurate usage.
| Error | Impact |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Thermometer Placement | False readings, incorrect superheat |
| Improper Gauge Usage | Inaccurate pressure, wrong superheat |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Superheat In Hvac Systems?
Superheat is the temperature increase above a refrigerant’s boiling point. It’s measured at the evaporator outlet. Superheat ensures efficient system performance and prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor.
Why Is Measuring Superheat Important?
Measuring superheat helps ensure optimal HVAC system performance. It prevents compressor damage and ensures efficient energy use. Proper superheat levels indicate the system is running correctly.
How Do You Measure Superheat?
To measure superheat, use a thermometer and pressure gauge. Measure the suction line temperature and evaporator pressure. Convert pressure to temperature using a refrigerant chart. Subtract the converted temperature from the measured temperature.
What Tools Are Needed To Measure Superheat?
To measure superheat, you need a thermometer and a pressure gauge. These tools are essential for accurate readings. A refrigerant pressure-temperature chart is also necessary.
Conclusion
Measuring superheat is crucial for HVAC system efficiency. Follow the steps to ensure accurate readings and optimal performance. Use the right tools and techniques for best results. Regularly check your system to prevent issues. Stay informed and maintain your equipment for long-term benefits.
Proper superheat measurement ensures energy savings and system longevity.
