High superheat and low subcooling typically indicate an undercharged air conditioning system. This often results from insufficient refrigerant levels.
High superheat occurs when the refrigerant gas is too warm before it enters the compressor. Low subcooling means the liquid refrigerant has not been sufficiently cooled before entering the evaporator. These conditions can lead to inefficient cooling and potential compressor damage.
Technicians often diagnose this issue by measuring refrigerant pressures and temperatures. Correcting it usually involves adding refrigerant to the system. Proper refrigerant levels ensure optimal performance and longevity of the air conditioning unit. Regular maintenance can prevent these issues and improve overall system efficiency. Keep an eye on these indicators to maintain a well-functioning HVAC system.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Basics Of Hvac Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding superheat and subcooling is crucial in the HVAC industry. These concepts ensure systems run efficiently. They also help in diagnosing potential issues. Here, we explain the basics of these terms.
Superheat Definition
Superheat refers to the temperature of a vapor above its boiling point. It is crucial in preventing liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. To calculate superheat, subtract the boiling point of the refrigerant from its current temperature.
- Evaporator Superheat: Measured at the outlet of the evaporator.
- Total Superheat: Measured at the compressor inlet.
Example calculation:
Superheat = Current temperature - Boiling pointIf the current temperature is 55°F and the boiling point is 45°F:
Superheat = 55°F - 45°F = 10°FSubcooling Definition
Subcooling refers to the temperature of a liquid below its condensation point. It ensures the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the expansion valve. To calculate subcooling, subtract the current temperature from the condensation point.
- Condenser Subcooling: Measured at the outlet of the condenser.
Example calculation:
Subcooling = Condensation point - Current temperatureIf the condensation point is 105°F and the current temperature is 95°F:
Subcooling = 105°F - 95°F = 10°FAccurate superheat and subcooling measurements help technicians maintain system efficiency. They also prevent damage to components.
Importance Of Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding superheat and subcooling is crucial for HVAC systems. These two factors ensure efficient operation and prevent damage. Correct levels maintain system health and performance.
System Efficiency
Proper superheat and subcooling ensure the system runs efficiently. Superheat measures the extra heat added to refrigerant vapor. This process prevents liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. Subcooling measures how much the liquid refrigerant is cooled below its boiling point. This ensures the refrigerant is fully condensed before entering the expansion valve.
Both superheat and subcooling are vital for system efficiency. Incorrect levels can lead to poor cooling performance. Proper levels reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
Preventing Compressor Damage
Maintaining correct superheat levels protects the compressor. Low superheat can cause liquid refrigerant to enter the compressor. This leads to potential compressor damage and costly repairs.
Correct subcooling levels ensure the refrigerant is properly condensed. Insufficient subcooling can cause vapor to enter the expansion valve. This can lead to inefficient operation and potential system failure.
Regular checks on superheat and subcooling levels are essential. This helps in preventing compressor damage and ensures long-term system reliability.
Common Causes Of High Superheat
Understanding the common causes of high superheat in HVAC systems is crucial. High superheat often signals issues that can compromise system efficiency. Below, we explore some of these common causes.
Low Refrigerant Levels
Low refrigerant levels can lead to high superheat. This occurs when there is insufficient refrigerant to absorb heat effectively. As a result, the refrigerant vaporizes too early, causing high superheat.
Here are some reasons for low refrigerant levels:
- Leaks in the system
- Improper charging during maintenance
- Natural loss over time
To diagnose low refrigerant levels, technicians often use pressure gauges and temperature readings. Addressing the root cause of low refrigerant is essential for optimal system performance.
Restricted Evaporator Coils
Restricted evaporator coils can also cause high superheat. This happens when airflow over the coils is hindered. Restricted airflow means less heat is absorbed, leading to higher superheat levels.
Common reasons for restricted evaporator coils include:
- Dirty coils due to dust and debris
- Blocked air filters that reduce airflow
- Frost buildup on the coils
Regular maintenance can prevent these issues. Cleaning coils and replacing air filters are simple steps to ensure efficient system operation.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Refrigerant Levels | Insufficient refrigerant leading to early vaporization |
| Restricted Evaporator Coils | Hindered airflow reducing heat absorption |
By understanding these common causes, you can take proactive steps. This helps maintain your HVAC system’s efficiency and longevity.

Credit: hvacrschool.com
Common Causes Of Low Subcooling
Understanding the common causes of low subcooling can help maintain your HVAC system’s efficiency. Low subcooling indicates that the refrigerant has not lost enough heat. This can lead to inefficient cooling and potential system damage. Below are some common causes of low subcooling:
Overcharged System
An overcharged system often leads to low subcooling. When too much refrigerant is in the system, it reduces the space for heat exchange. This can cause the refrigerant to remain too warm, leading to low subcooling.
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| High Pressure | The system shows higher-than-normal pressure readings. |
| Poor Cooling | The cooling efficiency drops significantly. |
Malfunctioning Expansion Valve
A malfunctioning expansion valve can also cause low subcooling. This valve regulates refrigerant flow into the evaporator. If it fails, the refrigerant flow becomes irregular. This can result in insufficient cooling and low subcooling.
- Irregular Flow: The valve may allow too much or too little refrigerant.
- Temperature Issues: The system may not reach the desired temperature.
Identifying these issues early can save you time and money. Regular maintenance checks are essential for a healthy HVAC system. Always consult a professional for accurate diagnosis and repair.
Symptoms Of High Superheat And Low Subcooling
Understanding the symptoms of high superheat and low subcooling is crucial for maintaining an efficient HVAC system. These conditions can indicate significant issues, leading to poor performance and potential damage. Recognizing these symptoms early helps in troubleshooting and repairing your system effectively.
Inefficient Cooling
One of the primary symptoms of high superheat and low subcooling is inefficient cooling. The air conditioner struggles to lower the room temperature. You may notice rooms taking longer to cool. The HVAC system runs for extended periods. The desired comfort levels are hard to achieve.
Here’s a summary of the inefficient cooling symptoms:
- Longer cooling times
- Extended running periods
- Difficulty in achieving desired temperatures
Unusual Noises
Unusual noises are another symptom of high superheat and low subcooling. The HVAC system may produce strange sounds. These noises can include banging, clanking, or hissing. They indicate issues within the system.
Here’s a list of the common unusual noises you might hear:
- Banging
- Clanking
- Hissing
These noises are often a sign of internal problems. Addressing them promptly can prevent further damage.
Diagnostic Tools For Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding superheat and subcooling is crucial in HVAC systems. Diagnosing these parameters accurately ensures optimal system performance. Let’s explore essential diagnostic tools.
Manifold Gauges
Manifold gauges are vital for measuring refrigerant pressure. They help diagnose superheat and subcooling issues.
- High-pressure gauge: Measures discharge pressure.
- Low-pressure gauge: Measures suction pressure.
- Connect these gauges to service ports for accurate readings.
Manifold gauges display pressure in PSI or bars. Use the readings to calculate superheat and subcooling. Note the temperature difference for accurate diagnosis.
Digital Thermometers
Digital thermometers measure temperature with high accuracy. They are essential for superheat and subcooling calculations.
- Clamp-on thermometers: Attach to pipes for surface temperature.
- Probe thermometers: Insert into ducts or refrigerant lines.
- Ensure proper contact for precise readings.
Digital thermometers offer quick and reliable temperature data. Use these readings to calculate the exact superheat and subcooling values.
| Tool | Usage |
|---|---|
| Manifold Gauges | Measure refrigerant pressure |
| Digital Thermometers | Measure temperature accurately |
These tools are indispensable for diagnosing HVAC systems. Ensure their accuracy for effective troubleshooting.
Step-by-step Troubleshooting Guide
High superheat and low subcooling can cause HVAC systems to malfunction. This guide provides a clear path to solve these issues. Follow these steps to restore your system’s efficiency.
Identifying The Problem
First, you need to identify the symptoms. High superheat means the refrigerant is not absorbing enough heat. Low subcooling means the refrigerant is not cooling enough before entering the evaporator.
Use your gauges to measure the superheat and subcooling levels. Compare these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| High Superheat | Low refrigerant level, TXV malfunction |
| Low Subcooling | Excess refrigerant, inefficient condenser |
Correcting Refrigerant Levels
Once you identify the problem, the next step is to correct the refrigerant levels. Follow these steps:
- Turn off the HVAC system.
- Attach gauges to the service ports.
- Remove excess refrigerant if subcooling is low.
- Add refrigerant if superheat is high.
Ensure the system is rechecked after adjustments. This will confirm the levels are within the specified range.
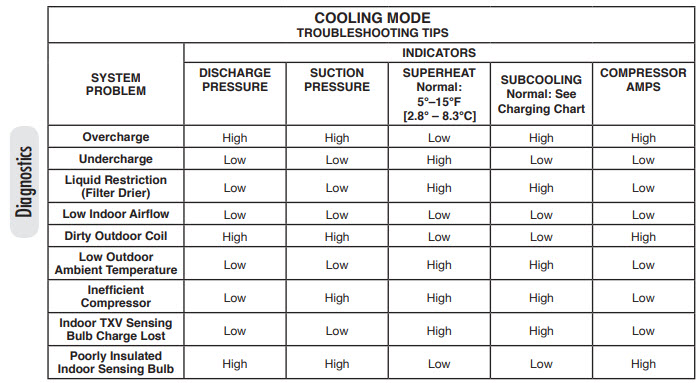
Credit: abrwholesalers.com
Preventative Maintenance Tips
Maintaining your HVAC system can help avoid issues like high superheat and low subcooling. Regular check-ups and proper installation are crucial. Here are some preventative maintenance tips to ensure your system runs smoothly.
Regular System Checks
Conducting regular system checks can identify potential problems early. Follow these steps:
- Inspect refrigerant levels monthly.
- Check for leaks every quarter.
- Monitor system pressure weekly.
- Clean filters every month.
- Check electrical connections regularly.
Use a checklist for consistency. Document findings for future reference.
Proper Installation Practices
Ensuring proper installation practices can prevent issues like high superheat and low subcooling. Follow these guidelines:
- Hire qualified technicians.
- Use manufacturer-recommended parts.
- Ensure proper refrigerant charge.
- Check for correct airflow direction.
- Verify system calibration.
A well-installed system runs efficiently. It reduces the risk of future issues.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect refrigerant levels | Monthly |
| Check for leaks | Quarterly |
| Monitor system pressure | Weekly |
| Clean filters | Monthly |
| Check electrical connections | Regularly |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes High Superheat In Hvac Systems?
High superheat often indicates insufficient refrigerant or a malfunctioning expansion valve. It can also result from restricted airflow or dirty coils.
How To Fix Low Subcooling Issues?
To fix low subcooling, check for refrigerant leaks, ensure proper airflow, and clean condenser coils. Adjust refrigerant levels if necessary.
Why Is Superheat Important?
Superheat ensures that only vapor enters the compressor, preventing liquid damage. It also helps in efficient energy transfer.
What Does Low Subcooling Indicate?
Low subcooling often indicates undercharged refrigerant or an oversized metering device. It can affect cooling efficiency and system performance.
Conclusion
Understanding high superheat and low subcooling is crucial for efficient HVAC systems. Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and energy savings. Regular checks can prevent costly repairs and improve system longevity. Prioritize routine inspections to maintain balance and efficiency. Keep your HVAC system running smoothly by addressing superheat and subcooling issues promptly.
