Low superheat causes include refrigerant overcharge and restricted airflow. These issues can lead to inefficient cooling and system damage.
Low superheat is a critical issue in HVAC systems. It often indicates problems such as refrigerant overcharge or restricted airflow. These problems can result in inefficient cooling and potential damage to the system. Diagnosing low superheat early can prevent costly repairs and ensure the system operates efficiently.
Regular maintenance checks can help identify and rectify these issues promptly. Technicians need to measure superheat accurately to diagnose problems effectively. Addressing low superheat promptly improves system performance and longevity. Homeowners should schedule regular HVAC inspections to keep their systems in optimal condition. Proper airflow and refrigerant levels are crucial for efficient HVAC operation.
Introduction To Superheat
Understanding superheat is crucial in HVAC systems. It helps in diagnosing problems and ensuring efficiency. This section will introduce you to the concept of superheat.
Definition And Importance
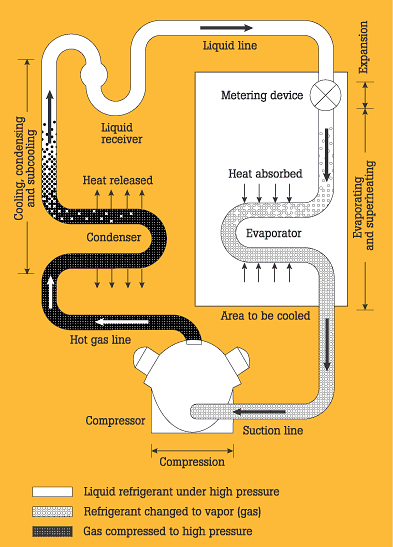
Superheat is the difference between the actual temperature of a vapor and its saturation temperature. In simpler terms, it’s the extra heat added to a vapor after it has fully evaporated.
Superheat is important because it ensures that the refrigerant is in a vapor state when it reaches the compressor. This prevents liquid from entering the compressor, which can cause serious damage.
Role In Hvac Systems
Superheat plays a vital role in HVAC systems. It helps in controlling the cooling process and maintaining system efficiency. Let’s look at its roles:
- Prevents liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor
- Ensures efficient heat transfer
- Helps in diagnosing system issues
Superheat is measured at two points: the evaporator outlet and the compressor inlet. These measurements help in fine-tuning the system for optimal performance.
Table: Superheat Measurement Points
| Measurement Point | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Evaporator Outlet | Ensures refrigerant is fully vaporized |
| Compressor Inlet | Prevents liquid from entering the compressor |
Understanding and monitoring superheat is essential for any HVAC technician. It ensures the system runs efficiently and safely.
Causes Of Low Superheat
Understanding the causes of low superheat is crucial for maintaining efficient HVAC systems. Low superheat can lead to inefficient cooling and potential damage to the compressor. Let’s explore some of the primary causes of this issue.
Refrigerant Overcharge
A common cause of low superheat is refrigerant overcharge. When there is too much refrigerant in the system, it can result in low superheat readings. This excess refrigerant causes the evaporator coil to be flooded with liquid, reducing its ability to absorb heat effectively.
- System overfilled with refrigerant
- Leads to liquid refrigerant entering the compressor
- Can cause damage to the compressor
To address this, you need to ensure the refrigerant levels are within the manufacturer’s specifications. Using the correct tools to measure and adjust refrigerant levels is essential.
Restricted Airflow
Restricted airflow is another significant cause of low superheat. When airflow is restricted, the evaporator coil cannot absorb enough heat. This results in the refrigerant not being fully vaporized, which lowers the superheat.
Common causes of restricted airflow include:
- Dirty air filters
- Blocked or closed vents
- Obstructed ductwork
Regular maintenance, such as changing air filters and ensuring vents and ducts are clear, can help prevent restricted airflow. Keeping the system clean and well-maintained is key to avoiding low superheat issues.
Symptoms Of Low Superheat
Understanding the symptoms of low superheat is crucial for HVAC maintenance. Low superheat affects system efficiency and can cause damage. Recognizing the symptoms early prevents costly repairs.
Inefficient Cooling
One of the first signs of low superheat is inefficient cooling. The system struggles to maintain the set temperature. This results in longer running times and higher energy bills.
A table below highlights the comparison between normal and low superheat conditions:
| Condition | Normal Superheat | Low Superheat |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Stable | Unstable |
| Energy Consumption | Optimal | High |
Frost On Evaporator Coils
Frost on evaporator coils is another indicator of low superheat. Frost buildup restricts airflow and reduces cooling efficiency. This happens because the refrigerant doesn’t evaporate properly.
- Restricted airflow
- Reduced cooling efficiency
- Potential damage to the compressor
Addressing frost issues quickly can prevent further damage. Always keep an eye on the evaporator coils for early signs of frost.

Credit: hvacrschool.com
Impact On Hvac Efficiency
Low superheat in HVAC systems can significantly affect efficiency. A system with low superheat means that the refrigerant is not absorbing enough heat. This inefficiency can lead to various issues, including higher energy consumption and performance degradation.
Energy Consumption
Low superheat leads to higher energy consumption. The compressor works harder to maintain the desired temperature. This extra effort results in increased power usage. In turn, this inflates utility bills.
Consider this: a system with low superheat cycles on and off more frequently. Each cycle uses additional energy. This can quickly add up, causing a significant increase in energy costs.
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Frequent Cycling | Increases energy consumption |
| Harder Compressor Work | Higher utility bills |
Performance Degradation
Low superheat also causes performance degradation. The system cannot remove enough heat from the space. This leads to less effective cooling or heating.
Several symptoms indicate performance degradation:
- Ineffective cooling or heating
- Frequent compressor shutdowns
- Inconsistent room temperatures
These symptoms can cause discomfort and reduce the lifespan of HVAC components. Regular maintenance can help identify and resolve low superheat issues. This ensures the system operates efficiently.
Potential Failures Due To Low Superheat
Low superheat in HVAC systems can lead to serious problems. It’s important to understand these potential failures. This ensures the longevity and efficiency of your system.
Compressor Damage
The compressor is the heart of the HVAC system. Low superheat can cause liquid refrigerant to enter the compressor. This liquid can cause severe compressor damage. Compressors are designed to compress gas, not liquid.
Liquid refrigerant can cause flood-back. This leads to the erosion of internal components. Over time, this erosion can lead to compressor failure. Replacing a compressor is costly and time-consuming.
| Issue | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor Damage | Low Superheat | Flood-back of liquid refrigerant |
| Erosion | Liquid Refrigerant | Component Failure |
System Short Cycling
Low superheat can also lead to system short cycling. This means the system turns on and off frequently. Short cycling stresses the system.
Short cycling impacts the system’s efficiency. It causes increased wear and tear on components. This can lead to premature failure of parts. The system may require more frequent repairs.
- Frequent on and off cycles
- Increased wear and tear
- Premature failure of parts
Maintaining proper superheat levels is essential. It ensures the longevity and efficiency of your HVAC system. Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues.
Diagnosing Low Superheat
Diagnosing low superheat in an HVAC system is crucial. Low superheat can lead to inefficient cooling and potential damage. Understanding the correct steps and tools is vital for accurate diagnosis.
Tools And Instruments
To diagnose low superheat, you need specific tools:
- Digital Thermometer: Measures temperature accurately.
- Pressure Gauges: Measures system pressure.
- Refrigerant Scale: Weighs refrigerant accurately.
- Manifold Gauge Set: Checks pressure in the system.
Ensure all tools are calibrated for precise readings.
Step-by-step Process
Follow these steps to diagnose low superheat:
- Check the Thermostat: Ensure it’s set to the correct temperature.
- Inspect the Air Filter: A dirty filter can cause low superheat.
- Measure Indoor Temperature: Use a digital thermometer.
- Measure Suction Line Temperature: Place the thermometer on the suction line.
- Record Suction Pressure: Use the manifold gauge set.
- Convert Pressure to Temperature: Use a pressure-temperature chart.
- Calculate Superheat: Subtract suction line temperature from the pressure-converted temperature.
Compare the calculated superheat with the manufacturer’s recommendation.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Check the Thermostat |
| 2 | Inspect the Air Filter |
| 3 | Measure Indoor Temperature |
| 4 | Measure Suction Line Temperature |
| 5 | Record Suction Pressure |
| 6 | Convert Pressure to Temperature |
| 7 | Calculate Superheat |
Identifying the cause of low superheat helps in taking corrective actions. It ensures the HVAC system operates efficiently and safely.
Preventive Measures
Low superheat in HVAC systems can lead to serious problems. It is crucial to take preventive measures to maintain optimal performance and avoid costly repairs. Here are some effective strategies.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to preventing low superheat issues. Schedule routine inspections to identify potential problems early. This involves:
- Cleaning or replacing air filters.
- Checking refrigerant levels.
- Inspecting and cleaning coils.
- Ensuring proper airflow.
Regular maintenance keeps your HVAC system running smoothly. It also extends its lifespan.
Proper Installation
Proper installation is crucial for avoiding low superheat. Ensure the system is installed by certified professionals. Key steps include:
- Choosing the correct size unit.
- Ensuring proper refrigerant charge.
- Verifying correct airflow settings.
- Ensuring all connections are secure.
Correct installation can prevent many issues. It ensures your system operates efficiently from the start.
Both regular maintenance and proper installation are vital. They help maintain optimal superheat levels and system efficiency.
Credit: www.achrnews.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Low Superheat?
Low superheat means reduced temperature difference between the refrigerant and its boiling point. It can indicate refrigerant overcharge or system issues.
What Causes Low Superheat In Hvac Systems?
Low superheat can be caused by overcharged refrigerant, a dirty evaporator coil, or malfunctioning thermostatic expansion valves (TXV).
How Does Low Superheat Affect System Performance?
Low superheat can lead to poor cooling efficiency and potential compressor damage due to liquid refrigerant return.
Can Low Superheat Damage The Compressor?
Yes, low superheat can cause liquid refrigerant to return to the compressor, leading to damage or failure.
Conclusion
Understanding low superheat is crucial for maintaining HVAC system efficiency. It can prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal performance. Regular monitoring can help detect issues early. Always consult a professional for accurate diagnosis and solutions. Prioritizing system health ensures longevity and comfort.
Keep your HVAC system running smoothly with proper maintenance practices.
