High superheat and high subcooling indicate potential issues in an HVAC system. These conditions suggest improper refrigerant levels or system restrictions.
High superheat occurs when the refrigerant vapor is excessively heated beyond its boiling point in the evaporator coil. High subcooling happens when the refrigerant liquid is overly cooled below its condensation point in the condenser coil. Both conditions can lead to inefficient system performance and increased energy consumption.
Properly diagnosing and addressing these issues is essential for maintaining system efficiency and longevity. Technicians must check for refrigerant leaks, blockages, or improper charge levels. Ensuring the HVAC system operates within optimal parameters enhances performance and reduces operational costs. Regular maintenance can prevent these issues, keeping the system running smoothly.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Understanding Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding superheat and subcooling is essential for maintaining efficient HVAC systems. These terms refer to specific temperature conditions within the HVAC cycle. Correct management of these temperatures ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Definition And Importance
Superheat is the temperature of a vapor above its boiling point at a given pressure. It ensures that no liquid refrigerant returns to the compressor, preventing damage. Subcooling is the temperature of a liquid below its boiling point at a given pressure. It maximizes the efficiency of the refrigerant and prevents vapor bubbles in the liquid line.
| Term | Definition | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Superheat | Temperature of vapor above boiling point | Prevents liquid return to compressor |
| Subcooling | Temperature of liquid below boiling point | Maximizes refrigerant efficiency |
How They Affect Hvac Systems
High superheat indicates low refrigerant levels or poor heat exchange. This can lead to compressor overheating. It also reduces the efficiency of the HVAC system. Low superheat suggests excess refrigerant or insufficient heat absorption. This can cause liquid refrigerant to enter the compressor, causing damage.
- High superheat: Low refrigerant or poor heat exchange
- Low superheat: Excess refrigerant or insufficient heat absorption
High subcooling means the refrigerant is over-condensed. This indicates an overcharged system or restricted airflow. Low subcooling shows that the refrigerant is not fully condensed. This can be due to undercharging or excessive heat load.
- High subcooling: Over-condensed refrigerant
- Low subcooling: Incomplete condensation
Monitoring superheat and subcooling helps diagnose and resolve HVAC issues. Proper balance ensures the system runs efficiently.
Causes Of High Superheat
High superheat in HVAC systems can lead to various issues. Understanding its causes helps in maintaining system efficiency. Let’s explore the common causes of high superheat.
Low Refrigerant Charge
One major cause of high superheat is a low refrigerant charge. This means there isn’t enough refrigerant in the system.
- Insufficient refrigerant leads to improper cooling.
- Evaporator coil doesn’t get enough liquid refrigerant.
- Refrigerant boils off too quickly.
- Results in high superheat and poor system performance.
Ensuring the right refrigerant level helps maintain optimal superheat.
Airflow Issues
Another cause is improper airflow. Proper airflow is critical for system efficiency.
- Blocked air filters restrict airflow.
- Dirty evaporator coils reduce heat exchange.
- Fans or blowers not working properly.
Addressing these issues can help reduce high superheat.
| Problem | Effect |
|---|---|
| Low Refrigerant Charge | Improper Cooling |
| Blocked Air Filters | Restricted Airflow |
| Dirty Evaporator Coils | Poor Heat Exchange |
Causes Of High Subcooling
High subcooling in HVAC systems can cause issues. Understanding the causes helps in fixing them. Two main causes are overcharging refrigerant and condenser efficiency.
Overcharging Refrigerant
Overcharging refrigerant means adding too much refrigerant to the system. This can lead to high subcooling. When there is too much refrigerant, it cannot evaporate properly. The excess stays in the condenser, causing high subcooling.
- Too much refrigerant in the system
- Refrigerant cannot evaporate properly
- Excess refrigerant stays in the condenser
Condenser Efficiency
The condenser plays a vital role in cooling the refrigerant. If the condenser is dirty or blocked, it can’t work efficiently. This can lead to high subcooling. A dirty condenser reduces heat transfer, trapping more refrigerant in the liquid state.
- Dirty condenser reduces heat transfer
- Blocked condenser traps refrigerant
- Inefficient condenser causes high subcooling
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Overcharging Refrigerant | High subcooling due to excess refrigerant |
| Condenser Efficiency | High subcooling due to poor heat transfer |
Symptoms Of Inefficient Hvac Systems
High superheat and high subcooling are signs of inefficient HVAC systems. These symptoms can lead to various problems in your home. Recognizing these signs early can help you take action quickly.
Inconsistent Temperature
One clear symptom is inconsistent temperature throughout your home. Some rooms may feel too hot, while others feel too cold. This imbalance can make your living space uncomfortable.
A table can help to illustrate the temperature differences:
| Room | Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|
| Living Room | 75 |
| Bedroom | 68 |
| Kitchen | 77 |
Inconsistent temperatures occur due to poor HVAC system efficiency. High superheat and high subcooling can cause these temperature imbalances.
Increased Energy Bills
Another symptom is increased energy bills. An inefficient HVAC system uses more energy to maintain desired temperatures. This increased energy usage directly affects your utility bills.
Consider these points:
- HVAC systems work harder with high superheat and high subcooling.
- Higher energy consumption results in higher costs.
- Regular maintenance can help reduce these costs.
Monitoring your energy bills can help identify inefficiencies. An unexpected rise in costs may indicate HVAC issues.
Addressing these symptoms promptly can improve your HVAC system’s performance. This leads to a more comfortable home and lower energy bills.
Measuring Superheat And Subcooling
Understanding how to measure superheat and subcooling is crucial for HVAC system efficiency. These measurements ensure systems operate correctly. This guide will explain the tools and steps needed.
Required Tools
- Manifold gauge set
- Thermometer or temperature probe
- Pressure-temperature chart
- Calculator
Step-by-step Process
- Attach the Manifold Gauges
Connect the manifold gauges to the system’s service ports. The blue hose connects to the low side, and the red hose connects to the high side.
- Measure the Suction Line Temperature
Use the thermometer to measure the temperature on the suction line. This line is usually insulated and near the compressor.
- Read the Low-Side Pressure
Check the low-side pressure on the manifold gauge. Note this reading.
- Find the Saturation Temperature
Use the pressure-temperature chart. Find the saturation temperature corresponding to the low-side pressure.
- Calculate Superheat
Subtract the saturation temperature from the suction line temperature. The result is your superheat.
Measurement Value Suction Line Temperature 45°F Saturation Temperature 35°F Superheat 10°F - Measure the Liquid Line Temperature
Use the thermometer to measure the temperature on the liquid line. This line is usually smaller and not insulated.
- Read the High-Side Pressure
Check the high-side pressure on the manifold gauge. Note this reading.
- Find the Saturation Temperature for the High Side
Use the pressure-temperature chart. Find the saturation temperature corresponding to the high-side pressure.
- Calculate Subcooling
Subtract the liquid line temperature from the high-side saturation temperature. The result is your subcooling.
Measurement Value Liquid Line Temperature 95°F High-Side Saturation Temperature 105°F Subcooling 10°F
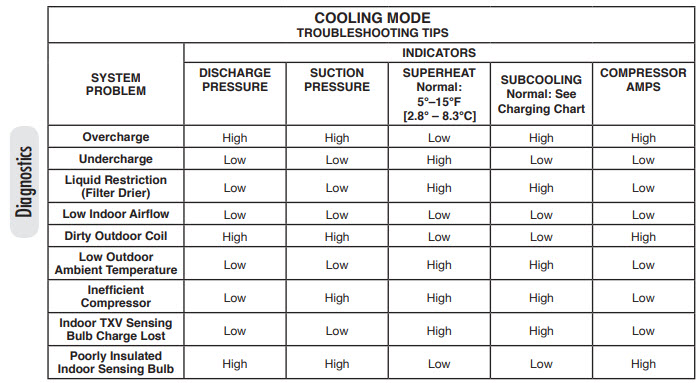
Credit: abrwholesalers.com
Optimizing Superheat Levels
Optimizing superheat levels ensures efficient refrigeration system performance. Proper superheat levels prevent compressor damage and increase system efficiency. This section provides actionable steps to achieve optimal superheat levels.
Adjusting Refrigerant Charge
First, check the refrigerant charge in the system. A correct charge is vital for optimal superheat. Too much or too little refrigerant affects performance.
- Measure the current refrigerant charge.
- Compare with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Add or remove refrigerant to match the required levels.
Balancing refrigerant levels ensures the system operates efficiently. This step prevents both high superheat and high subcooling.
Improving Airflow
Airflow affects superheat levels significantly. Proper airflow ensures the system functions correctly.
- Check air filters for dirt and blockages.
- Clean or replace dirty filters.
- Ensure all vents are open and unobstructed.
Good airflow results in better heat exchange. This helps maintain proper superheat levels.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Check refrigerant charge. |
| 2 | Adjust refrigerant as needed. |
| 3 | Ensure clean air filters. |
| 4 | Verify vents are open. |
Follow these steps to optimize your system. Efficient systems save energy and extend equipment life.
Optimizing Subcooling Levels
Optimizing subcooling levels is crucial for efficient HVAC systems. Proper subcooling ensures the system runs smoothly and saves energy. This section covers key aspects of optimizing subcooling levels.
Proper Refrigerant Charging
Proper refrigerant charging is essential. Incorrect refrigerant levels can cause high subcooling. Follow these steps for accurate charging:
- Use the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Measure ambient temperature.
- Check the superheat and subcooling levels.
- Adjust refrigerant levels accordingly.
Always use proper tools and equipment. Inaccurate tools can lead to errors. Regularly calibrate your tools for best results.
Enhancing Condenser Performance
Enhancing condenser performance helps maintain optimal subcooling. A well-functioning condenser removes heat efficiently. Follow these tips to enhance performance:
- Clean the condenser coils regularly.
- Ensure adequate airflow around the condenser.
- Check for blockages in the condenser unit.
- Maintain the correct fan speed.
Regular maintenance keeps the condenser in top shape. Schedule periodic checks to avoid issues.
Optimizing subcooling levels involves proper refrigerant charging and enhancing condenser performance. Keeping these systems in check ensures efficient operations and energy savings.
Maintaining Optimal Hvac Efficiency
Maintaining optimal HVAC efficiency is crucial for comfort and cost savings. High superheat and high subcooling can indicate problems in your HVAC system. These issues can lead to inefficient cooling, higher energy bills, and potential system failure. To ensure your HVAC system runs smoothly, follow these tips and guidelines.
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Clean or replace air filters monthly to ensure proper airflow.
- Inspect ductwork for leaks or blockages that can affect efficiency.
- Check thermostat settings to ensure your system is running correctly.
- Clean the outdoor unit regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Check refrigerant levels to ensure they are within the recommended range.
Professional Hvac Inspections
Scheduling regular professional inspections can help identify and fix issues early. A professional technician can provide a more thorough inspection and maintenance service.
- Inspect and clean coils to ensure efficient heat exchange.
- Check electrical connections to prevent potential hazards.
- Measure superheat and subcooling to ensure proper refrigerant charge.
- Test system controls to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Calibrate the thermostat for accurate temperature control.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean or replace air filters | Monthly |
| Inspect ductwork | Annually |
| Check thermostat settings | Seasonally |
| Clean the outdoor unit | Quarterly |
| Check refrigerant levels | Annually |
By following these tips and getting regular professional inspections, you can maintain optimal HVAC efficiency. This ensures your system runs smoothly, keeping your home comfortable and your energy bills low.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is High Superheat?
High superheat indicates that the refrigerant gas is absorbing more heat than usual. This can point to undercharged systems or airflow issues.
What Causes High Subcooling?
High subcooling occurs when the refrigerant is cooled excessively before entering the expansion valve. This could be due to overcharging or a restricted condenser.
How To Fix High Superheat?
To fix high superheat, check for refrigerant leaks, ensure proper airflow, and verify the system is correctly charged.
How To Reduce High Subcooling?
To reduce high subcooling, you may need to adjust the refrigerant charge or check for blockages in the condenser coil.
Conclusion
Understanding high superheat and high subcooling can optimize your HVAC system’s efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures longevity and performance. Addressing these issues promptly can save energy and costs. Stay informed and proactive with your HVAC care. This knowledge helps maintain a comfortable and efficient environment all year round.
